Transformation of Nairobi towards 3R (Robust, Reliable & Resilient) localisation of food systems and Energy savings through mitigating UHI
Long description
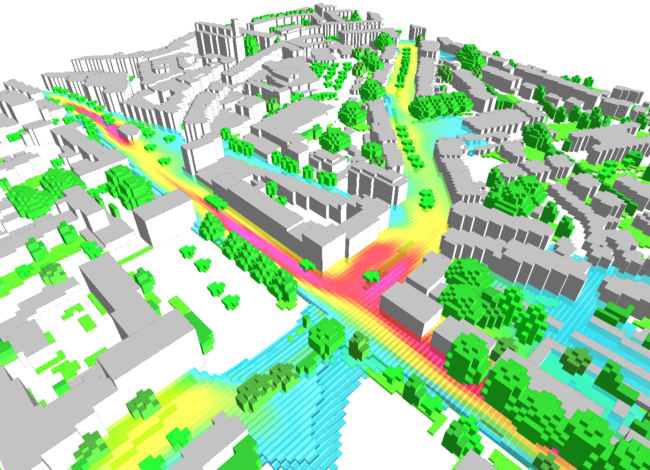
Rapid urbanisation led to a series of environmental problems, especially the formation of urban heat island (UHI) phenomenon, whereby urban regions experience warmer temperatures than their rural surroundings. UHI is the most illustrative sign of climate change in the current time of increasing urbanisation, leading to increased energy demands for cooling and transportation, poor outdoor microclimate as well as increased human thermal discomfort.
The project focused on five main urban domains (i.e. Local Climate Zones, urban design, planting design, landscape planning and conservation) which jointly are essential in understanding and achieving the transformation towards 3R (Robust, Reliable & Resilient) localization of food production systems and energy savings through edible planting designs as practical and effective UHI mitigation and adaptation strategy for Nairobi city.
The interdisciplinary project uses some urban climate models to simulate different spatial configurations of edible planting designs, green spaces and street orientations to develop adaptation prototype for each Local Climate Zone and revive the traditional landscape within Nairobi city. This will build on my previous research on the modelling of UHI and quantification of environmental amelioration effects of plant species.
We will create a website, make 3D physical models, print posters and run workshops to communicate the result to stakeholders. Results will include 3D models, 2D planting designs, adaptation atlases, and a list of edible plants and Planting designs showing the spatial configuration of the best green scenario for each Local climate zone, and a possibility of application to the whole city and other Kenyan cities.








Please login or create a profile to view comments